Carpal Tunnel Release with Ultrasound Guidance
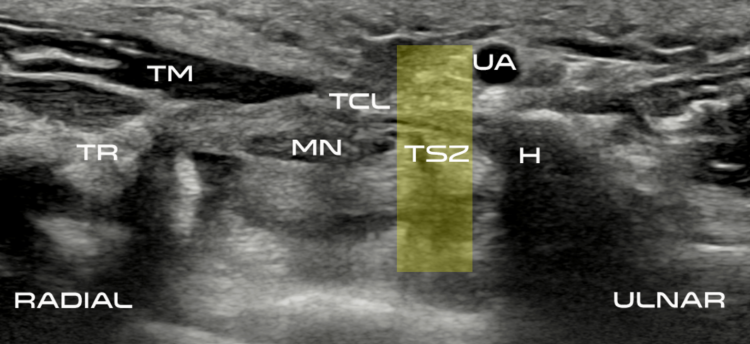
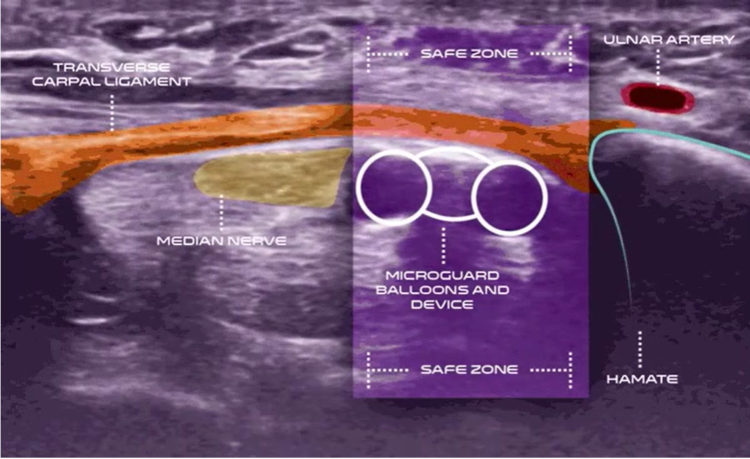
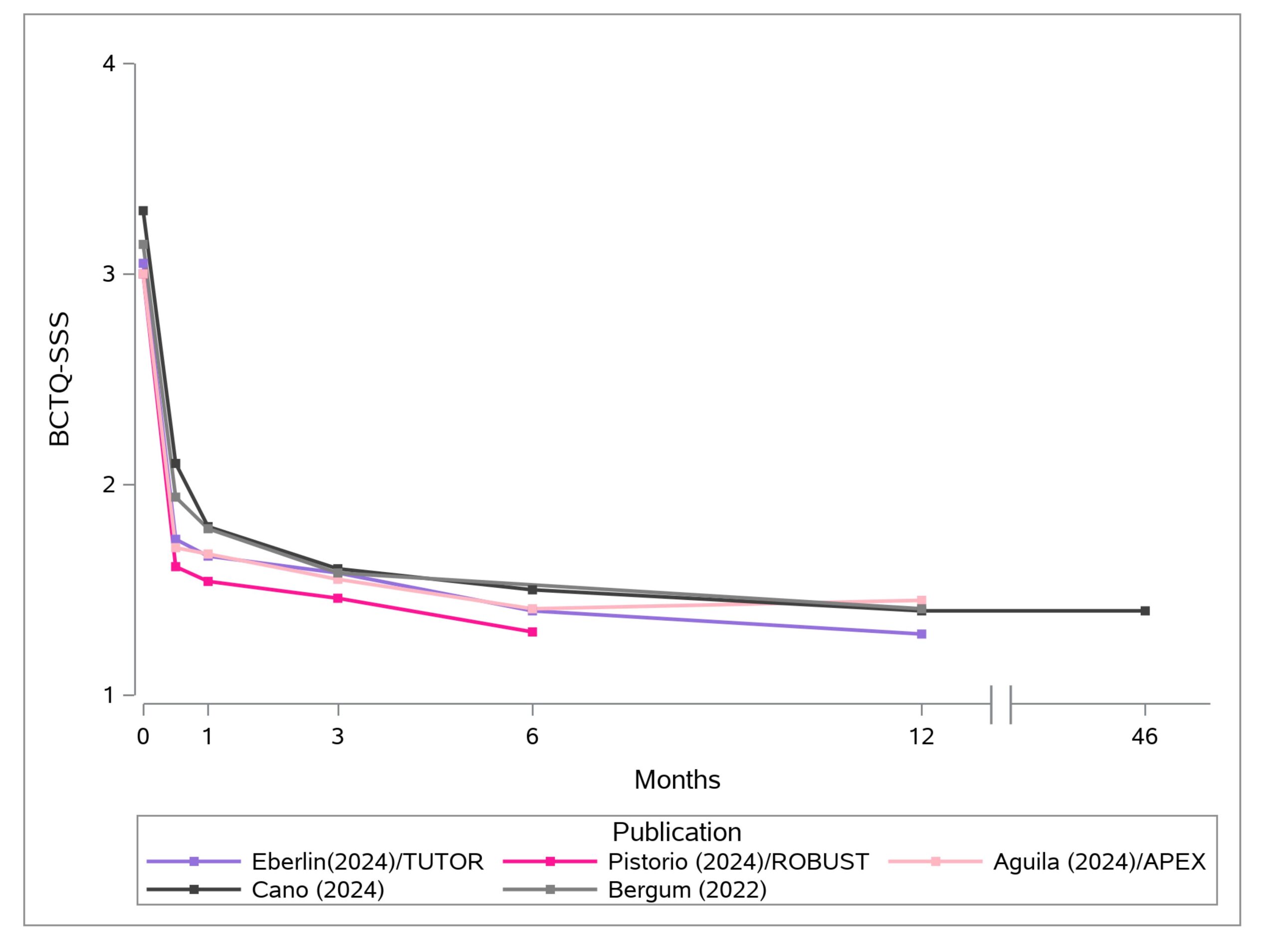
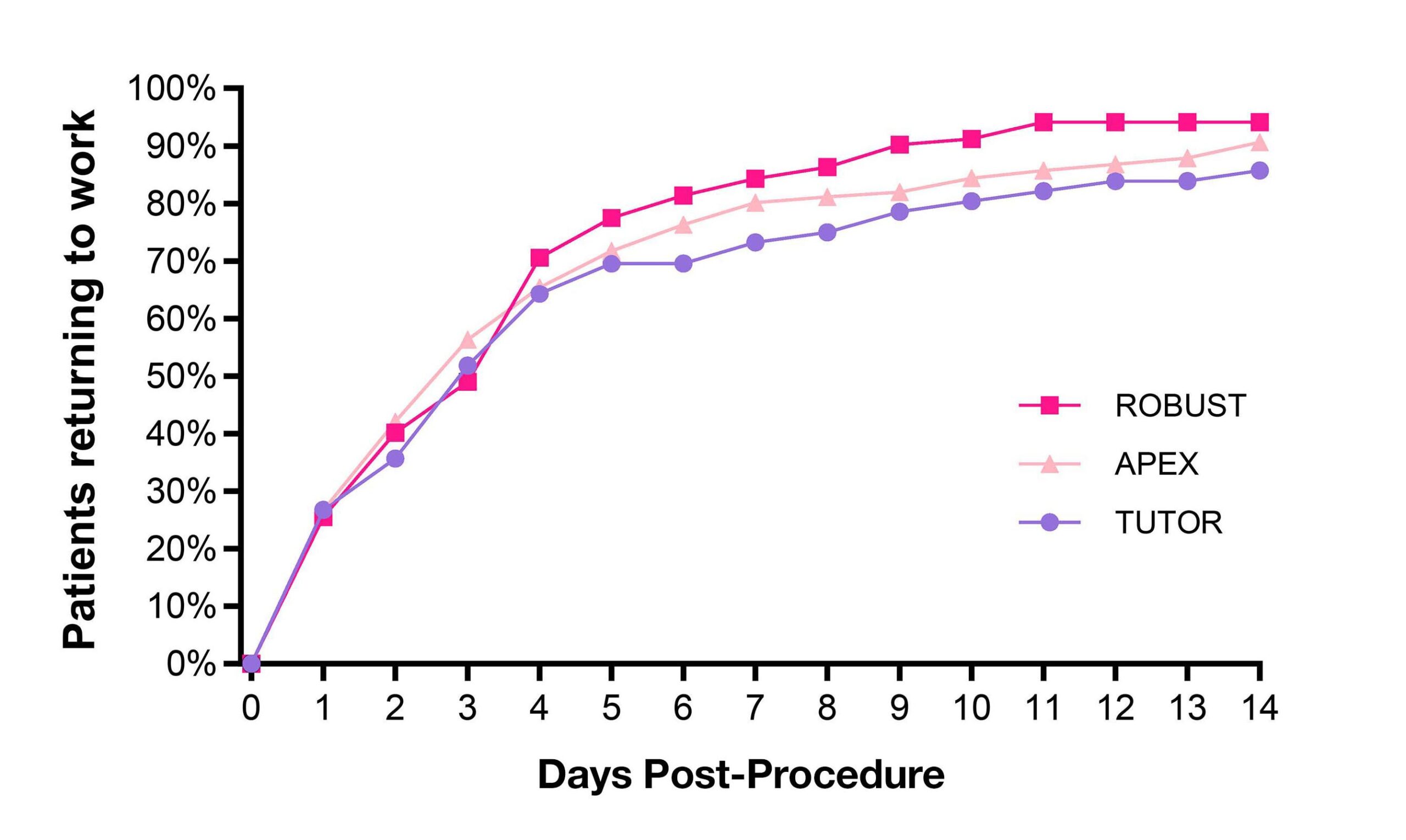
Carpal tunnel release with real-time ultrasound guidance (CTR-US) was initially described by Nakamichi in 1997.10, 11 Since then, over 30 peer reviewed publications have reported clinical results on over 3,000 hands (>2,500 patients) treated with CTR-US. 7, 11-22 The collective clinical success rate is over 95%, with these publications documenting the safety and effectiveness of CTR-US, an excellent safety profile, and the ability to perform the procedure in the office-based setting.7, 11-22